Home » Keywords: » formulating tips
Items Tagged with 'formulating tips'
ARTICLES
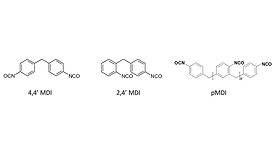
A New High-Performance Alternative to Cobalt Driers
A novel, cobalt-free drier featuring manganese neodecanoate and an amine ligand delivers faster drying times for alkyd coatings, reducing toxicity without compromising performance.
Read More
Keep the info flowing with our eNewsletters!
Get the latest industry updates tailored your way.
JOIN TODAY!Copyright ©2025. All Rights Reserved BNP Media.
Design, CMS, Hosting & Web Development :: ePublishing