The quest for improved scratch/abrasion-resistant coatings is a goal for many coatings formulators. Thousands of scratch-resistant coating applications are present in our everyday lives. Examples of these applications include coatings for wood floors, safety glasses, electronic displays, automotive finishes and polycarbonate panels. Improving the mar, scratch and/or abrasion in these transparent coating applications is a major challenge, particularly with regard to not affecting the other performance attributes of the coating.
Incorporation of inorganic fillers into coatings to improve mechanical properties is well known. Drawbacks associated with this approach can include loss of transparency, reduced coating flexibility, loss of impact resistance, increase in coating viscosity and appearance of defects. To overcome these defects, a filler material should impart improved scratch resistance without causing the aforementioned detriments. Nanomaterials have the potential to overcome many of these detriments because of their inherent small size and particle morphology. Maintaining transparency in a coating containing inorganic filler particles is a challenge. Four properties dictate the degree of transparency in a composite material: film thickness, filler concentration, filler particle size, and the difference in refractive index between the bulk coating and the filler particle.
Silica particles, colloidal or fumed, and clays are among the most widely studied inorganic fillers for improving the scratch/abrasion resistance of transparent coatings. These fillers are attractive from the standpoint that they do not adversely impact the transparency of coatings due to the fact that the refractive indices of these particles (fumed silica = 1.46, bentonite clay = 1.54) closely match those of most resin-based coatings. The drawback to silica-based fillers is that high concentrations of the particles are generally required to show a significant improvement in the scratch/abrasion resistance of a coating, and these high loadings can lead to various other formulation problems associated with viscosity, thixotropy and film formation.
The use of alumina particles in transparent coatings is much more limited even though alumina is significantly harder than silica-based materials, and as a scratch- and abrasion-resistant filler, higher performance at lower loadings is often observed. For alumina particle sizes greater than 100-nm, the high refractive index (1.72) results in significant light scattering and a hazy appearance in most clear coatings. Currently, only high-refractive-index coatings, such as the melamine-formaldehyde resins used in laminate production, can use submicron alumina for scratch resistance and maintain transparency.

Nanoparticle Production
To use alumina as scratch-resistant filler in transparent coatings, the particle size must be sufficiently small to overcome its refractive index mismatch. Nanophase Technologies Corp. (NTC) has developed the Physical Vapor Synthesis (PVS) process that is capable of producing metal oxide nanoparticles via a bottoms-up method starting from metallic feed. This process allows production of nonporous crystalline metal oxides having primary particle sizes less than 100 nm at economically viable rates with essentially no byproducts or waste streams.
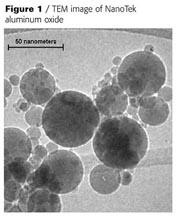
NTC produces two grades of aluminum oxide using the PVS process: NanoTek™ and NanoDur™ alumina. Both grades feature a mixture of g and d crystal phases and are spherical in shape, but the grades differ in terms of primary particle size. NanoTek alumina has a surface area of 35 m2/g corresponding to a mean particle size of 48 nm, whereas NanoDur alumina has a surface area of 45 m2/g with a mean particle size of 37 nm. A TEM image of NanoTek alumina is shown in Figure 1.

Nanoparticle Dispersion
For nanoparticles to be of use in transparent coatings, it is critical that aggregates present in the powder be dispersible to their primary particle size in the coating formulation to avoid rapid settling and excessive light scattering. In addition, it is critical that the dispersed primary particles avoid re-aggregation during the coating curing process.NTC has developed a proprietary particle dispersion stabilization process that involves specific surface treatments designed to yield nanoparticles that are compatible with a variety of different coating formulations. For example, stable dispersions of metal oxide nanoparticles can be prepared in solvents such as water, alcohols, polar and nonpolar hydrocarbons, plasticizers, and even directly in acrylate monomers with the appropriate surface-treatment process. These surface treatments allow solids levels of up to 60 wt% to be dispersed, and yet maintain a sufficiently low viscosity for ease of blending.
The use of highly concentrated, non-aggregated nanoparticle dispersions allows incorporation of the nanoparticles into a coating formulation without substantial dilution of the formulation with the dispersion liquid. This feature is particularly important in 100%-solids coating formulations wherein the nanoparticle is dispersed in one of the reactive monomers.

Nanoparticle Composites
Using concentrated dispersions of aluminum oxide nanoparticles in various solvents and reactive monomers, composites were prepared for a variety of transparent coating formulations including emulsion-based polyurethanes and polyacrylates; solventborne, two-component polyurethanes and melamine-polyols; and 100%-solids UV-curable coatings. Importantly, the alumina nanoparticles also featured surface treatments designed specifically for the formulation chemistry of the coating type in which it was dispersed.Nanoparticle coating composites were prepared using both the NanoTek and NanoDur grades of aluminum oxide in a solventborne transparent melamine-polyol coating to compare the haze of the two different particle sizes. The haze results are shown in Figure 2.
Three aspects of the haze data in Figure 2 are noteworthy. (1) As expected, the larger-particle-size NanoTek alumina (48 nm, mean) results in higher haze in the melamine-polyol nano-composite compared to those made with NanoDur alumina (37 nm, mean), at a given alumina loading level. (2) If transparency in a clear coating is defined as < 1% haze, it is apparent that the particle size of alumina used in the composite be no greater than 50 nm in order to maintain transparency. (3) Even with an alumina nanoparticle size grade of < 50 nm, improvement in scratch/abrasion resistance of the coating composite must be attainable with relatively low alumina loadings to stay within the transparency limit.

Scratch-Resistant Nanocomposites
To evaluate the performance of alumina nanoparticles as scratch-resistant fillers in a transparent coating, a nanocomposite was prepared with NanoDur alumina dispersed in a UV-curable coating formulation. The alumina nanoparticles were dispersed in 1,6-hexanediol diacrylate, a reactive monomer, at 30 wt%, and this dispersion was blended with a UV-curable formulation to provide composite coatings with variable levels of alumina particles between 0.2 and 2.0 wt%. These composites were subjected to a scratch test involving 200 double rubs with a 0000-grade steel wool pad and the level of scratching quantified by measuring the increase in haze due to the scratches. The performance of the alumina-containing composite coatings was compared with the neat coating without alumina particles. The results of this scratch study are shown in Figure 3.The performance of the alumina nanoparticles in Figure 3 is expressed as X times improvement in scratch resistance compared with the neat coating. It is evident the alumina nanoparticles significantly improve the performance of the UV-curable coating, up to a nine-fold improvement, even with very low levels of alumina incorporated in the composite.
The scratch-resistance properties of alumina nanoparticles were also compared with silica particles at equivalent loading levels. The silica particles are surface-treated and dispersed in 1,6-hexanediol diacrylate and were blended into the same UV-curable coating formulation as the alumina particles. The comparative performance is shown in Figure 4. As is evident in Figure 4, the alumina particles provide much better scratch-resistance protection for the UV-curable coating compared to the silica particles at equivalent particle loadings. The much harder alumina particles are superior at preventing steel wool scratching compared to the softer silica particles.
The scratch-resistance performance of alumina nanoparticles incorporated into a variety of other transparent coating compositions was also evaluated. A level of 1 wt% alumina particles was used in all cases, and the alumina particles were introduced in the coating formulations by dispersing the alumina at high concentration into the appropriate solvent used in the coating formulation, then blending into the formulation at a level to yield 1 wt% particles with respect to the total solids in the cured coating. The scratch-resistance performance was measured using the same steel wool scratch test as was applied to the UV-curable coatings. The results of this study are summarized in Figure 5.
Several features can be noted by comparing the relative alumina performance in different transparent coating formulations in Figure 5. First, there is a range of scratch improvement dependent upon the particular formulation within the coating class. For example, the scratch resistance of UV-curable coatings can be improved anywhere from five- to 10-fold with the incorporation of 1 wt% alumina, depending on the type and concentration of reactive acrylate components used in the formulation. Performance ranges for the melamine-based coatings, 2K polyurethane coatings, and emulsion-based coatings evaluated were also observed.
Within a given coating class, those formulations that resulted in harder/stiffer coatings tended to show greater improvement with alumina incorporation than did those formulations that lead to softer/more elastomeric coatings. In addition, transparent coating formulations that exhibit crosslinking upon curing, such as UV-curable, 2K polyurethane, and melamine-based coatings, showed greater improvement in their scratch resistance upon alumina nanoparticle incorporation compared to transparent coatings that do not crosslink but rather coalesce, such as emulsion-based coatings.
Summary
Due to the past unavailability of aluminum oxide that was less than 100 nanometers in average size, improvements in scratch-resistant coatings were limited. As demonstrated in the above examples, the use of nanomaterials in coating formulations can significantly improve scratch resistance. These improvements can be used in clear topcoats, ink-over-print varnishes and pigmented finishes. The commercial availability of nanoparticles will allow coating formulators to obtain new properties that were unachievable in the past, not only in scratch resistance but many other physical performance attributes.For more information, contact Russell "Bo" Kowalczyk, manager of Customer Service, phone 630/771.6709, e-mail bkowalczyk@nanophase.com.
Nanophase Technologies Forms Global Partnership with Altana Chemie AG
Nanophase Technologies Corp. has formed an exclusive global partnership with Altana Chemie AG, the specialty chemicals business of ALTANA AG, to supply certain nanomaterials for use in paints, coatings and plastics.The partnership will collaborate in developing innovative materials for specialty market areas, such as general industrial coatings, architectural coatings, coil coatings, automotive OEM and refinish coatings, printing inks, duroplastics and thermoplastics, consumer goods packaging, and electrical insulation applications.
The companies plan to start product co-development immediately, and expect initial market product introductions during late 2004.
In view of the exclusivity and the partnership's objectives, Altana has purchased 1,256,281 shares of Nanophase common stock at a purchase price of $7.96 per share, or an aggregate of $10 million in cash. These shares will be restricted and not registered for a period of two years. After this purchase, Nanophase has 17,371,814 shares of common stock outstanding, approximately 7% of which is now owned by Altana.
"This is a highly significant partnership for Nanophase," stated Dan Bilicki, Nanophase's vice president of sales and marketing. "We believe that there are immediate and long-term market opportunities that this partnership can successfully address. Nanophase looks forward to working closely with Altana, and expects that this relationship will drive profitable revenue growth for both companies."
"With this strategic investment ALTANA Chemie is taking a significant step into the field of nanotechnology. Nanocomposites will be a key driver in the future for innovative products in coatings, plastics or electrical insulation applications and will help to safeguard the leading competitive positions of our business units," said Dr. Matthias L. Wolfgruber, member of the Management Board of ALTANA, and CEO of ALTANA Chemie.




