Citrate Esters as Coalescents for Acrylic Dispersions

ilyast, Creatas Video+, via Getty Images.
Coalescing agents play an important role in the water-based paint and coatings industry with applications in a variety of different segments such as construction, packaging, automotive, marine, electronics, and furniture.
The main function of a coalescent is to guarantee a uniform and optimal film formation for the desired mechanical performance and chemical resistance, as well as aesthetic values like gloss and haze effects. The coalescing agent softens the polymer of the binder. After the application of an aqueous coating onto a surface, the water evaporates, causing the binder particles to draw together. Here, the coalescent takes effect, giving rise to the formation of a homogeneous film. This complex interaction is influenced by various factors, in particular the nature of the binder.
A majority of standard coalescing agents are considered volatile organic compounds (VOCs), i.e. those substances are not retained in the dried film. The advantage of their use is an increase in the film hardness after evaporation. However, high volatility has become an undesired effect due to regulatory concerns. VOCs contribute to emissions, and, due to their toxicological profile, cause hazardous conditions for paint manufacturers and processors, as well as consumers.
Regulations have become more strict, and there is a clear trend towards low-VOC or even zero-VOC formulations. Therefore, non-volatile coalescing agents are increasingly considered as alternatives to enhance film formation.
In this study, the performance of CITROFOL® citrate esters as coalescing agents for clear coats for metal and wood applications, as well as an architectural paint formulation, was investigated and the results were compared to those of standard coalescing agents.

The citrate esters are non-VOC, bio-based, odorless, and label free, which is an advantage compared to conventional coalescing agents.

No citrate esters showed weight loss over a period of 28 days, whereas the conventional coalescing agents EA1, EA2, and GE1 evaporated over time.
The study revealed that the citrate esters showed broad compatibility with different types of dispersions and applications (Table 2). For the clear coats the pendulum hardness (according to König DIN EN ISO 1522), adhesion (cross-cut according to DIN EN ISO 2409), and gloss (glossmeter in accordance with DIN EN ISO 2813:2015-02) were measured.
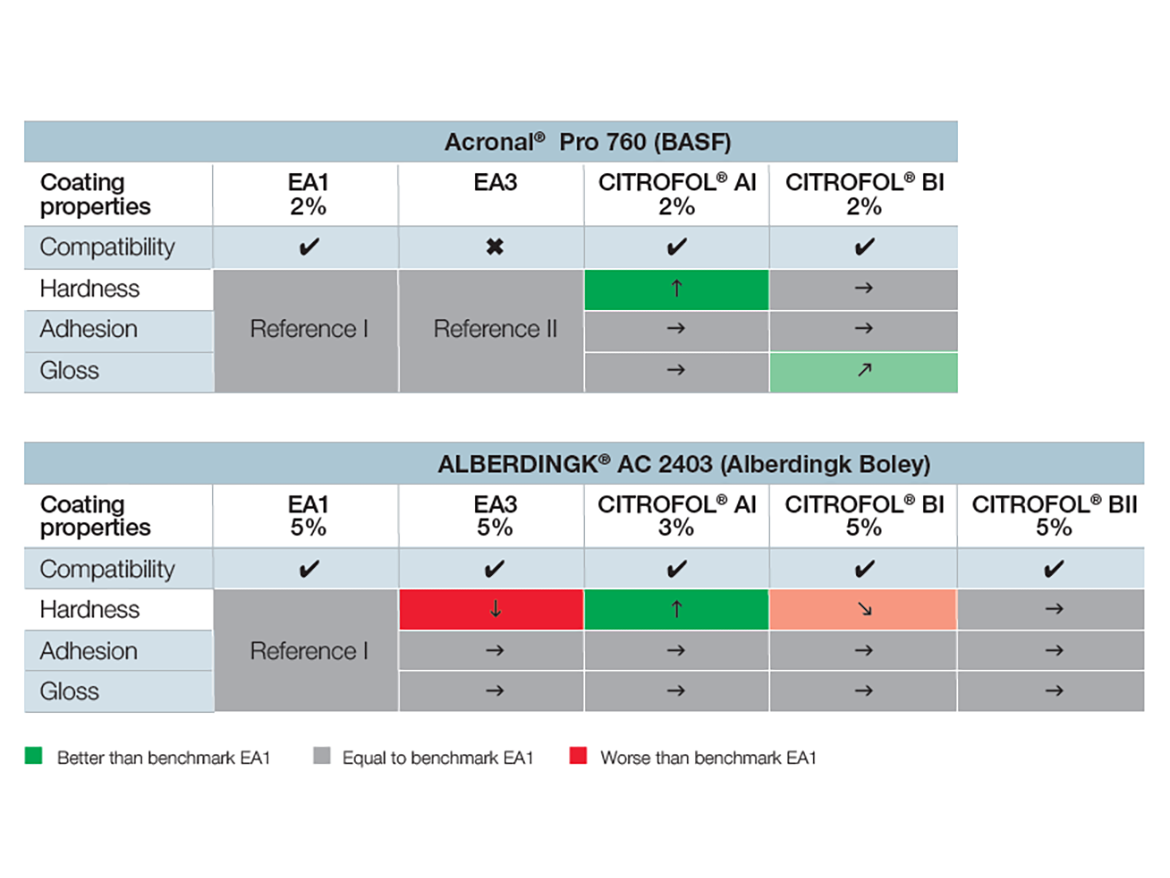
The results prove that citrate esters exhibited the same or even better properties compared to standard coalescing agents regarding all crucial processing requirements and end-product properties.
A standard, flat architectural paint formulation acted as the base, and the different coalescents were tested at a 2.4% addition rate.
In this test set up, wet scrub resistance (according to DIN EN ISO 11998:2006-10), drying behavior (according to DIN EN ISO 9117-5:2012), viscosity (plate-plate rheometer), as well as levelling and sagging (Leneta draw-down blade) were tested.

The deviations between the tested coalescing agents for the dried paint formulations were not significant. The values obtained for pendulum hardness and gloss were very low. This corresponds to the typical appearance of an interior, flat paint formulation.
In the case of wet-scrub resistance, the thickness loss after 200 scrubbing cycles varied between 3.1 μm and 3.6 μm for all samples, which is quite low. Therefore, all tested formulations fall into abrasion class 1 according to DIN EN 13300. These values show that no citrate esters have a negative impact on the wet-scrub resistance of the paint formulations.
In regards to drying behavior, the formulations with EA1, CITROFOL AI, and CITROFOL BII yielded identical results, which are quantified in degrees of drying as mentioned above. The degree of drying DS1 (dust dry) was reached after 15 minutes. DS4 was achieved after 30 minutes, and DS7 after 60 minutes. Very similar results were obtained for levelling and sagging, and for viscosity measurements, too.
Conclusion
Bio-degradable citrate esters have excellent toxicological and eco-toxicological profiles, and provide good versatility and compatibility with numerous polymers. They are characterized by highly efficient solvation, low migration, and non-VOC attributes. They are could be used for sensitive products like toys, medical devices, food packaging, pharmaceutical applications, and personal care. Moreover, all CITROFOL esters are vegan, kosher, halal, and non-GMO.
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!






